In the near future, replacing the battery inside an iPhone won’t be a risk-prone, complex, and messy affair with glue everywhere. According to The Information, Apple is exploring a new technology that will make it easier for people to remove the battery unit inside their iPhones, making replacements and repairs more convenient.
Here’s the detail right from the horse’s mouth: “The new technology—known as electrically induced adhesive debonding—involves encasing the battery in metal, rather than foil as it is currently. That would allow people to dislodge the battery from the chassis by administering a small jolt of electricity to the battery, the people said.”
Apple is making the change because it has had a change of heart regarding the glue problem that has irked repair professionals and DIY enthusiasts for years. Even the folks over at iFixit had to write a whole article titled “Why Electronics Rely on Glue—and Why They Shouldn’t” to shed more light on the situation.
“On a 2020 iPhone model, that process can take up to two hours of disassembly, an hour to clean up corrosion damage from liquids, and then another hour of application to replace the adhesive. Not an easy fix,” noted the article.
Why Apple is doing this

Why is this happening now? It’s due to the E.U. and its crusade toward sustainability and a cleaner future. Last year, the European Commission notified the Batteries Regulation, which, among other things, wants to handle the situation with more responsibility and in a way that doesn’t worsen the electronic waste problem. The following are the core tenets:
Targets for recycling efficiency, material recovery and recycled content will be introduced gradually from 2025 onwards. All collected waste batteries will have to be recycled and high levels of recovery will have to be achieved.
Starting in 2027, consumers will be able to remove and replace the portable batteries in their electronic products at any time of the life cycle.
Portable batteries incorporated in appliances shall be readily removable and replaceable by the end-user or by independent operators during the lifetime of the appliance, if the batteries have a shorter lifetime than the appliance, or at the latest at the end of the lifetime of the appliance.
“In a big success for the right to repair, all new portable devices and light means of transport put on the market will now have to be designed with replaceable batteries,” Cristina Ganapini, coordinator of the Right to Repair (Europe), said back then. You can read the complete proposal here (PDF).
A bit of ionic magic
So, how does Apple’s shift to the enigma called “electrically induced adhesive debonding” work? Adhesives capable of forming strong bonds while allowing for quick and convenient electricity-fueled separation are in high demand. Such technology is particularly valuable in urgent situations or for components requiring frequent disassembly, says a research paper published in the Materials Today Communications journal.


The electrical and electronics sectors have a pressing need for electrically removable adhesives to enable the installation and maintenance of fragile electronic parts. Using conductive adhesives that respond to electricity for attaching components to circuit boards would significantly simplify the process of removing and replacing faulty elements.
An additional benefit of these adhesives is their ability to be activated remotely, removing the necessity for direct physical contact with the bonded parts. Right now, the glues used in smartphone assembly rely on high temperatures for melting and removal. The technique described above does the same job, but uses electrical stimulus instead of heat.
Shifting to electricity offers a promising solution that avoids many challenges. This method relies on adding ionic components, such as dissolved salts or ionic liquids, into the adhesive mixture. These additives add ion-based conductivity to the glue, and as a result, it becomes responsive to electrical stimulation.
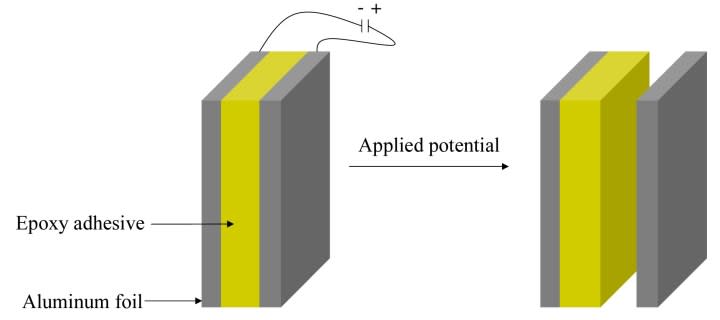

Voltage-activated debonding can reduce the risk of mechanical, thermal, or chemical damage to the internal components of a phone. However, the whole approach mandates using conductive substrates like metals or materials that can be coated with a conductive layer.
Once there, the debonding process can be started by applying a voltage across the two bonded surfaces. These electrically responsive adhesives are currently attracting a healthy amount of interest in the aerospace and electronics segments due to their potential applications and advantages over traditional bonding methods. iPhones could end up being the biggest adopters of this promising technology in the near future.
You can read more about the electrical adhesion and debonding process at a microscopic level in this research paper that was published in the Advanced Materials Interfaces journal here, and this fantastic thesis was submitted to the Sweden-based School of Chemical Science and Engineering Kungliga Tekniska Högskolan. You can read more about the whole technique in the context of recycling at the Royal Society of Chemistry.


















